Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory virus that mostly affects infants, old age, and individuals with poor immune systems. Common symptoms are cough, fever, and shortness of breath. This virus spreads through respiratory droplets and can cause illnesses such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia.
Table of contents:
- Symptoms and Causes of HMPV Infections
- HMPV vs covid-19
- Is HMPV a serious disease?
- Treatment and Prevention of (HMPV)
- How many people get HMPV?
- How long does it take to recover from human metapneumovirus?
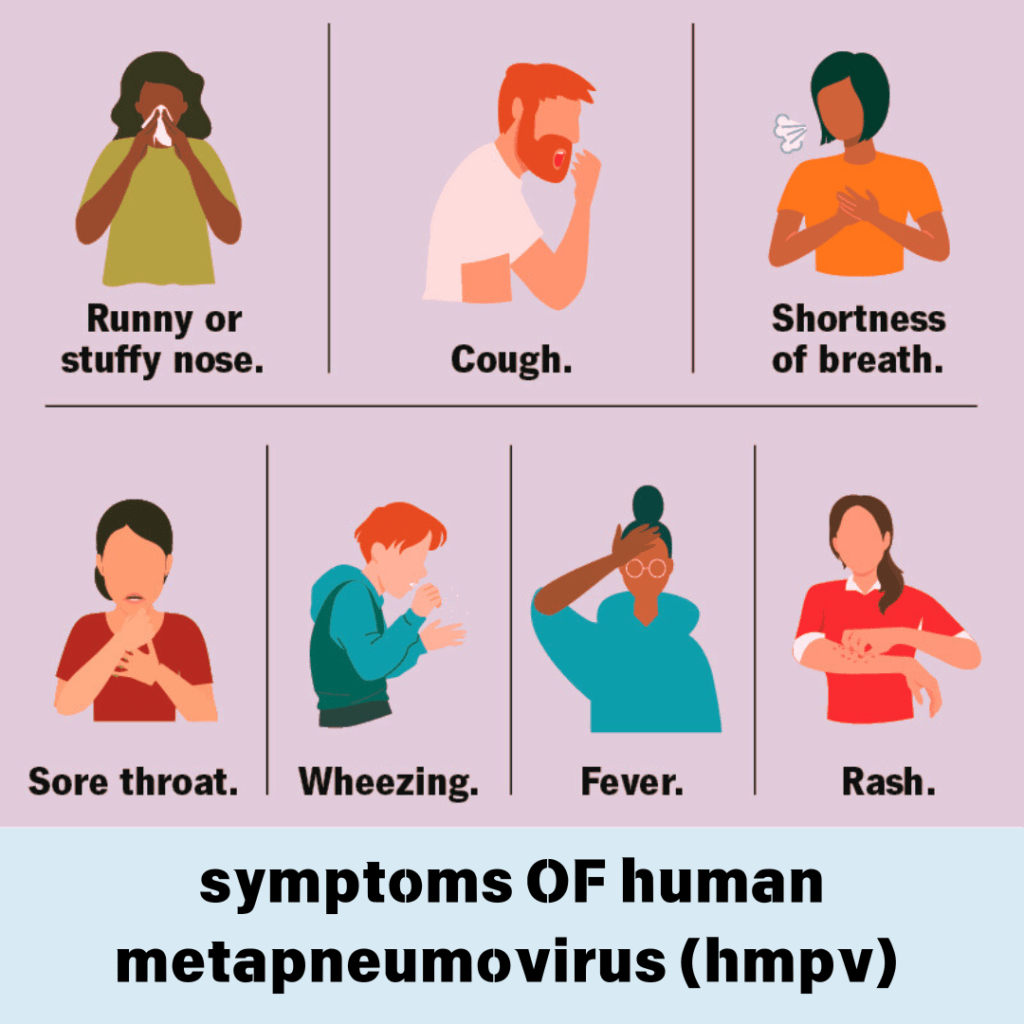
Symptoms and Causes of HMPV Infections:
- Cough: Either dry or productive.
- Fever: Low-grade fever that might become worse.
- Runny Nose: One of the first signs of infection
- Wheezing: Heavy breathing, which is more typical in children
- Shortness of Breath: Which may worsen over time.
- Sore Throat: Mild discomfort in the throat.
- Fatigue: A general feeling of tiredness and weakness.
HMPV vs covid-19
Here’s a more concise comparison table between HMPV and COVID-19:
| Feature | HMPV | COVID-19 |
|---|---|---|
| Causative Virus | Human Metapneumovirus | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Symptoms | Cough, fever, runny nose, wheezing, fatigue | Fever, cough, fatigue, loss of taste/smell, difficulty breathing |
| Severity | Mild, can cause bronchiolitis or pneumonia | Ranges from mild to severe, can cause pneumonia and death |
| Transmission | Respiratory droplets | Respiratory droplets and aerosols |
| Incubation Period | 3-6 days | 2-14 days |
| Risk Groups | Children, older people, immunocompromised | older, immunocompromised, underlying conditions |
| Diagnosis | PCR, viral cultures | PCR, antigen tests, RT-PCR |
| Treatment | Symptom relief | Antivirals, steroids, vaccines, supportive care |
| Prevention | Hygiene, avoiding contact | Vaccines, masks, social distancing |
| Vaccination | No vaccine, Yet | Multiple vaccines available |
Is HMPV a serious disease?
HMPV is usually not severe for healthy individuals because it typically causes a cold-like symptom that spontaneously resolves with supportive treatment. But yes, it can be severe in those populations at risk, such as small children, older adults, and people with poor immunity, because it could cause such things as bronchiolitis or pneumonia and necessitate hospital admission.
Treatment and Prevention of Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
Treatment for HMPV:
There is no specific antiviral treatment. Symptom relief includes:
- Fever management (acetaminophen or ibuprofen)
- Hydration
- Cough relief (OTC medications)
- Severe cases may require hospitalization and oxygen support.
Prevention of HMPV:
- Wash hands regularly.
- Avoid close contact with sick individuals.
- Cover coughs and sneezes.
- Disinfect frequently touched surfaces.
- Stay home when sick to prevent spreading the virus.
Note: No vaccine is currently available for HMPV.
How many people get HMPV?
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a common respiratory virus, with studies indicating that over 90% of individuals have been infected by age 5–10.
In children under 5 years old, HMPV is detected in approximately 3%–10% of hospitalizations for acute lower respiratory tract infections.
Recent data from the United States shows that 1.94% of individuals tested for respiratory illnesses were positive for HMPV in the last week of December 2024.
In China, HMPV was linked to 6.2% of positive respiratory illness tests and 5.4% of respiratory illness hospitalizations in late 2024.
These figures highlight that HMPV is a prevalent virus, especially among young children, and can lead to significant respiratory illnesses.
How long does it take to recover from human metapneumovirus?
Most people get over Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) in 1 to 2 weeks.
In milder cases, cough and congestion symptoms will begin to subside within 7–10 days.
-Bad cases, especially in vulnerable groups like young children, older people, and those with weak immune systems, may take longer and might require 2–3 weeks for full recovery, especially if a hospital stay is required for breathing support.
Recovery from HMPV is determined by the severity of the infection and the general health of the patient.
Conclusion on Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is an RNA virus and a viral respiratory infection characterized by cough, fever, and wheezing. HMPV mainly affects infants, the old, and the immunosuppressed people. HMPV is transmitted by means of respiratory droplets and is not a bacterial infection. No specific antiviral treatment exists, but supportive treatment is administered for symptom control. Good hygiene and avoidance of infected contacts are the prevention measures. Not a mainstream virus, HMPV can still provide considerable respiratory illness during seasonal outbreaks.


